Characteristics and applications
Torque sensor resistance principle
The torque sensors use the resistance principle to measure torque and force bidirectionally, with good linearity and negligible hysteresis. These sensors allow the measurement of torque ranging from less than 0.1 Nm to as high as 1000 Nm.
They are widely used in robots for handling parts in machining centers, presses, and measurement stations, providing an ideal automation solution that is convenient, accurate, repeatable, and reliable!
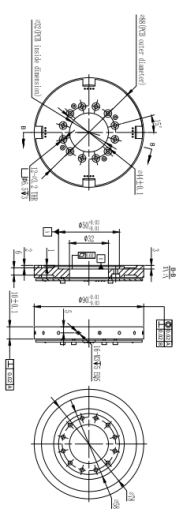
Rated range | Nominal (rated) torque Mnom | 110N.m |
Output sensitivity | Nominal (rated) sensitivity | 0.075~3.925mV/V |
| Nonlinearity | Non-linearity | 1.0%F.S. |
| Hysteresis | Hysteresis | 1.0%F.S. |
| Repeatability | Repeatability | 1.0%F.S. |
| Creep (30 minutes) | Creep(5min) | 1.0%F.S. |
| Temperature coefficient of sensitivity drift | Temp.effect on output | 0.05%F.S./10℃ |
| Temperature coefficient of zero drift | Temp.effect on zero | 0.05%F.S./10℃ |
Insulation resistance | Insulation | ≥5000MΩ/100VDC |
Excitation voltage | Recommended excitation | 5V |
Temperature compensation range | Compensated temp range | -10~40℃ |
Operating temperature range | Operation temp range | -10-60℃ |
Safe overload | Safe overload | 120%F.S. |
Ultimate overload | Ultimate overload | 150%F.S. |
Protection level | Protection class | IP64 |
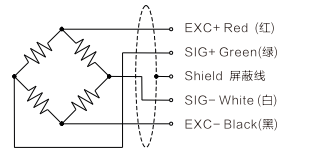
Wiring diagram |
 |